The glittering world of jewellery has long been a target for fraudsters and criminals seeking to exploit its high-value, portable nature. As the industry grapples with evolving threats, innovative technologies emerge as powerful allies in the fight against fraud. Blockchain and asset tokenisation are at the forefront of this technological revolution, offering unprecedented levels of transparency, traceability, and security. Let’s delve into how these cutting-edge solutions are reshaping the fraud prevention landscape in the jewellery sector.
With its dazzling array of precious metals and gemstones, the jewellery industry has always been an attractive target for illicit activities. From money laundering to counterfeiting, the challenges jewellers and regulators face are manifold. Blockchain and jewellery tokenization is proving to be a game-changer in the fight against fraud. Creating an immutable record of transactions offers a level of transparency and traceability. Meanwhile, asset tokenisation – creating digital representations of physical assets – is revolutionising how we track and trade valuable items.
The Current Landscape of Fraud in the Jewellery Industry
The jewellery sector has long been a prime target for fraudulent activities, owing to its products’ high value and portability. From counterfeit gems to money laundering schemes, the industry faces many challenges threatening its integrity and reputation.
- One of the most prevalent forms of fraud in the jewellery trade is selling counterfeit or misrepresented items. Unscrupulous dealers may pass off synthetic gems as natural or inflate the quality grades of diamonds and other precious stones. This not only deceives consumers but also undermines trust in the entire industry.
- Money laundering is another significant concern. The high value and easy transportability of jewellery make it an attractive vehicle for criminals seeking to legitimise ill-gotten gains. Complex international supply chains can further complicate efforts to trace the origin of funds used in jewellery purchases.
- Theft and insurance fraud also plague the industry. High-profile heists often make headlines, but smaller-scale thefts and fraudulent insurance claims are more common and equally damaging. These incidents result in financial losses and drive up insurance premiums for honest businesses.
- E-commerce platforms have become breeding grounds for fraudsters selling counterfeit or non-existent items. Cybercriminals may also target jewellery businesses’ online payment systems, putting customer data at risk.
Paper certifications and physical inspections, two traditional methods of thwarting these frauds, are becoming less and less effective in the face of increasingly complex criminal tactics. This is where blockchain and asset tokenisation enter the picture, offering innovative solutions to age-old problems.
Understanding Blockchain Technology

Blockchain technology is fundamentally a decentralised digital ledger. It’s a system that records transactions across multiple computers so that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively. This unique characteristic makes blockchain an incredibly powerful tool that ensures transparency and security in various industries, including jewellery.
At its core, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. When a transaction occurs, it’s broadcast to this network and must be validated by most participants. A new ‘block’ of data is created by joining two transactions once they have been validated, adding them to the current ‘chain’ of blocks, hence the term ‘blockchain’.
If someone attempts to alter a transaction, it would require changing not just that specific block but all subsequent blocks in the chain – a task that’s practically impossible given the system’s distributed nature. The decentralised nature of blockchain means that no one entity has control over the entire chain. Instead, all participants collectively retain control. Eliminating the risks associated with centralised systems, such as single points of failure or vulnerability to targeted attacks.
What is the Role of Blockchain in the Jewellery Industry?
Blockchain is capable of creating an immutable record of a gem’s journey from mine to market. Each transaction – from extraction to cutting, polishing, and eventual sale – can be recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and verifiable chain of custody.
This level of transparency can minimise the risk of fraud drastically. For instance, passing off synthetic gems as natural becomes much harder when every step of the gem’s journey is recorded on an unalterable ledger. Similarly, the provenance of precious metals can be tracked, making it more difficult for conflict minerals to enter the supply chain. Blockchain can complete more efficient and secure transactions. Smart contracts, can automate a variety of jewelry-related tasks, including insurance claims and supply chain management.
As we continue to explore blockchain’s applications in the jewellery industry, we’ll see how this technology is not just a tool for fraud prevention but a catalyst for transforming entire business models and creating additional opportunities for growth.
Asset Tokenisation: Digitising Physical Assets
Asset tokenisation is a groundbreaking concept rapidly gaining traction across various industries, including the jewellery sector. At its core, tokenisation involves creating a digital representation—or token—of a physical asset on a blockchain. This process effectively bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds, opening up new possibilities for valuing, trading, and securing high-value items like jewellery.
What is the Role of Asset Tokenisation in the Jewellery Industry?
In the jewellery industry, asset tokenisation can be applied to individual pieces, collections, or even entire inventories. Each token represents a specific asset or fraction of an asset and contains detailed information about its characteristics, provenance, and ownership history. This digital representation is recorded onto a blockchain, ensuring its authenticity and immutability.
- One key advantage of asset tokenisation is the enhanced liquidity it brings to traditionally illiquid assets. High-value jewellery pieces, which might typically take months or years to sell, can be divided into smaller, more accessible units through tokenisation.
- Tokenisation also simplifies the process of transferring ownership. Instead of the complex paperwork and physical transfers associated with traditional jewellery sales, ownership can be transferred instantly and securely through the blockchain.
- From a fraud prevention perspective, tokenisation offers several benefits. Each token carries a complete history of the asset it represents, making it extremely difficult to introduce counterfeit items into the market. The transparency blockchain provides ensures that transactions are visible and verifiable, deterring fraudulent activities.
- Moreover, tokenisation can enhance the traceability of precious materials throughout the supply chain. By tokenising raw materials at the extraction point, their journey through cutting, polishing, and manufacturing can be tracked with unprecedented accuracy. This level of traceability not only helps prevent fraud but also supports ethical sourcing initiatives.
- Asset tokenisation also opens up new possibilities for insurance and financing in the jewellery industry. Tokenised assets can be more easily used as collateral for loans, as their value and provenance are established on the blockchain. Insurance policies can be linked directly to tokenised assets, streamlining the claims process and reducing the risk of insurance fraud.
Blockchain Solutions for Jewellery Authentication
Authentication is a critical concern in the jewellery industry, where a piece’s value often lies in its genuineness and provenance. Blockchain technology offers innovative solutions to this age-old challenge, providing certainty and transparency that traditional methods simply can’t match.
One of the primary applications of blockchain in jewellery authentication is the creation of digital certificates. Unlike paper certificates, which can be forged or lost, blockchain-based certificates are immutable and easily verifiable. Each certificate is stored on the blockchain and contains detailed information about the jewellery piece, including its origin, characteristics, and ownership history.
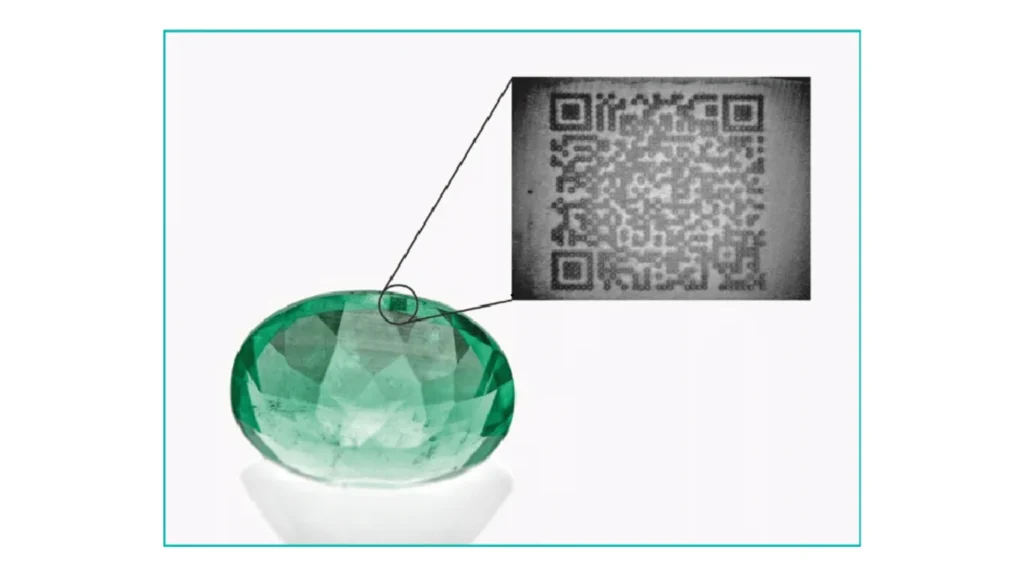

These digital certificates can be accessed via a unique identifier, such as a QR code engraved on the jewellery piece. When scanned, this code provides instant access to the item’s history, from its origin at the mine to its current ownership. This level of transparency deters fraud and enhances the value of authentic pieces by providing irrefutable proof of their provenance.
Blockchain can also be implemented to create a digital copy of each piece of jewellery. This virtual representation contains all the physical characteristics of the item, including detailed measurements, gemstone qualities, and even 3D scans. Any attempt to replace the original with a counterfeit would be immediately apparent compared to this digital twin.
Blockchain solutions can integrate data from gemological laboratories directly onto the ledger for gemstones. Each stone’s unique characteristics, such as its cut, clarity, and colour, can be recorded and linked to its blockchain certificate. This makes it extremely difficult for fraudsters to pass off lower-quality stones as higher-grade ones. It can also enhance the authentication process for vintage and antique jewellery. By creating a digital record of a piece’s history, including previous owners, restoration work, and appraisals, blockchain can help establish the authenticity of these often-valuable items.
Traceability and Supply Chain Management
The jewellery industry’s supply chain is notoriously complex, often spanning multiple countries and involving numerous intermediaries. This complexity has historically made it challenging to ensure ethical sourcing and prevent the infiltration of conflict minerals or synthetic gems. Blockchain technology, however, is proving to be a game-changer in this arena, offering unprecedented levels of traceability and transparency.
At its core, blockchain-enabled supply chain management creates an immutable record of each step in a jewellery piece’s journey from mine to market. This starts at the extraction point, where raw materials are first tokenised and entered into the blockchain. Each subsequent step – sorting, cutting, polishing, manufacturing, and distribution – is recorded, creating a complete and verifiable chain of custody.
This level of traceability offers several benefits. Firstly, it becomes much more complicated for unethical or illegal materials to enter the supply chain. Conflict diamonds, for instance, can be more easily identified and excluded. This helps companies comply with regulations like the Kimberley Process and meets the growing consumer demand for ethically sourced products.
Blockchain also enables real-time tracking of inventory throughout the supply chain, reducing incidents of theft and loss, as discrepancies can be immediately identified and investigated. It also improves efficiency by providing all stakeholders with a single, trusted view of the supply chain, reducing delays and disputes.
For consumers, blockchain-enabled traceability means the ability to verify the entire history of a piece of jewellery. Through a QR code or entering an identifier, customers can access all of the information about their purchase, from the origin of the gemstones to the craftsmanship involved in its creation. This transparency builds trust and also enhances the piece’s perceived value.
Blockchain-based supply chain management also opens up new possibilities for collaboration within the industry. Providing a shared, trusted platform for data exchange can foster closer relationships between miners, manufacturers, retailers, and even regulators.
Combating Money Laundering with Blockchain
At its core, blockchain’s ability to create an immutable, transparent record of transactions makes it inherently resistant to money laundering attempts.
One key application of blockchain in anti-money laundering (AML) efforts is in customer due diligence and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes. Blockchain-based identity verification systems can create secure, tamper-proof digital identities for customers.
Moreover, blockchain can facilitate the secure and privacy-preserving sharing of KYC information between different entities. This can reduce the time and cost associated with customer onboarding while enhancing the effectiveness of AML checks. Furthermore, blockchain can enhance the traceability of funds throughout the jewellery supply chain. by tokenising assets and recording all transactions on the blockchain, it becomes much easier to follow the movement of money and identify any attempts to introduce illicit cash into the system.
Enhancing Insurance and Risk Management

One of the primary applications of blockchain in this area is creating more accurate and verifiable valuations. By recording the complete history of a jewellery piece on the blockchain—including its origin, characteristics, and ownership transfers—insurers can have a much clearer picture of its true value.
Blockchain can also streamline the claims process. All relevant information about the insured item is readily available on the blockchain when a claim is made. Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain records makes it much harder for fraudulent claims to succeed.
A lot of insurance policy processes can be automated with the use of smart contracts. For example, a smart contract might automatically pay out if specific predetermined criteria are satisfied, like a confirmed theft report. This decreases the likelihood of disputes and expedites the claims procedure.
Blockchain and Asset Tokenisation
Combined with blockchain, asset tokenisation opens up new possibilities for fractional insurance. High-value pieces could be tokenised and insured in fractions, allowing for more flexible and affordable insurance options. This could make comprehensive insurance more accessible to more jewellery owners.
Blockchain can also enhance risk management in the supply chain. By providing real-time inventory tracking, it becomes easier to identify and mitigate risks at various points in the chain. For instance, if a particular route or supplier is associated with a higher theft risk, this can be quickly identified and addressed.
Moreover, blockchain can facilitate more effective risk information sharing between insurers, retailers, and law enforcement agencies. A shared blockchain could create a comprehensive database of stolen or lost items, making it harder for thieves to resell stolen jewellery and potentially aiding recovery efforts.
For vintage and antique jewellery, blockchain can provide a secure and verifiable record of an item’s provenance and history. This can be particularly valuable for insurance, as it offers clear evidence of an item’s authenticity and value. Additionally, blockchain-based technologies can enhance regulatory compliance. These solutions can assist companies in proving their compliance with industry standards and best practices by offering a transparent audit record of all transactions and insurance-related activity.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in the Jewellery Industry
One of the primary challenges is the issue of interoperability. Currently, there are multiple blockchain platforms and protocols in use, which don’t always communicate effectively with each other. This can create silos of information, potentially limiting the effectiveness of blockchain-based solutions across the industry.
Another major hurdle is the ‘garbage in, garbage out’ problem.Blockchain can guarantee that data is unchangeable once it is recorded, but it cannot assure that data is accurate when it is first entered.. If incorrect or fraudulent information is initially entered into the blockchain, it becomes part of the permanent record.
Another concern is the energy consumption that some blockchain networks come iwth, particularly those using Proof of Work consensus mechanisms. As the jewellery industry increasingly focuses on sustainability, blockchain technology’s environmental impact must be carefully considered. However, more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms are being developed and implemented.
Privacy and data protection present another challenge. While blockchain’s transparency is often touted as a benefit, there are situations where businesses or individuals may not want all information to be publicly visible. Balancing transparency with privacy requirements is an ongoing challenge in blockchain implementation.
User adoption and education represent another hurdle. For blockchain solutions to be effective, they must be widely adopted across the industry. This requires significant education and training efforts, not just for businesses but also for consumers who will be interacting with these new systems.
Finally, there’s the challenge of scalability. A blockchain’s ledger size increases with the number of transactions it records, which results in longer transaction times and more expenses. Various solutions to this problem are being developed, but scalability remains a concern for widespread blockchain adoption.
Conclusion – The Glittering Future of Blockchain in Jewellery
As we’ve explored throughout this article, blockchain technology and asset tokenisation are poised to revolutionise the jewellery industry. They offer innovative solutions to age-old challenges and open up exciting new possibilities. From enhancing authenticity and traceability to enabling new business models and customer experiences, these technologies are set to reshape every facet of the jewellery trade.
The potential for blockchain to combat fraud and enhance security in the industry cannot be overstated. By creating immutable records of a jewellery piece’s journey from mine to market, blockchain offers unprecedented transparency and traceability. This helps prevent fraud and meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products.
Asset tokenisation, meanwhile, is democratising access to high-value jewellery investments and enabling new forms of ownership and trading. This could increase liquidity in the market and open up new revenue streams for businesses in the sector.
However, as with any emerging technology, there are challenges to overcome. For blockchain to realise its full potential in the jewellery sector, issues of interoperability, data protection, and regulatory ambiguity need to be resolved. Moreover, widespread adoption will require significant education and investment across the sector.
Ultimately, blockchain and asset tokenisation are not just tools for enhancing security and efficiency in the jewellery industry—they’re catalysts for innovation and transformation. As we stand on the cusp of this blockchain-powered revolution, one thing is clear: the world of fine jewellery is set to sparkle brighter than ever before, illuminated by the transformative power of blockchain technology.